Climate Terminology
Change brings new terminology, and this is a brief overview of some terms now entering the vocabulary that are used to describe climate technology and the environment.
Carbon-neutral energy: energy that is produced without emitting greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
CO2e: carbon dioxide equivalents—adding up all emissions and converting them to carbon dioxide units. This takes into account a wide range of greenhouse gases, such as methane, where each unit of methane released equals 80 units of carbon dioxide.
Conventional power: “energy that comes from the burning of fossil fuels including coal, natural gas and oil. These fuels all have environmental costs from mining, drilling and extraction and emit greenhouse gases.” This includes energy from coal, oil, and natural gas.
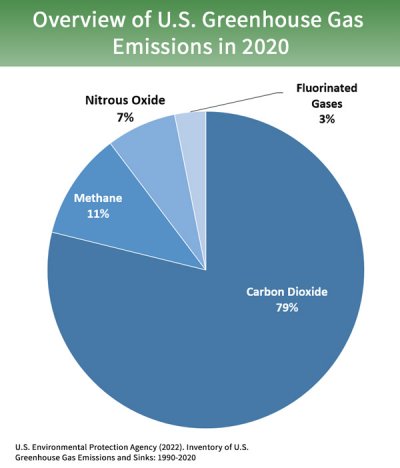
Greenhouse gases: “Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere.” These include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases.
LEED: Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, a sustainable building design that meets specific criteria. “available for virtually all building types, LEED provides a framework for healthy, efficient, and cost-saving green buildings.”
Renewable energy: “Renewable energy is electricity produced by fuel sources that renew themselves and do not diminish when humans tap them for power. Think the sun, the wind, plants and the heat at the Earth's core. These include electricity from solar panels, wind turbines, hydroelectric Renewable energy is dams and what's known as biomass, which is burning wood, crop waste or garbage.” This includes energy from wind, solar, all hydro, geothermal, and biomass.
